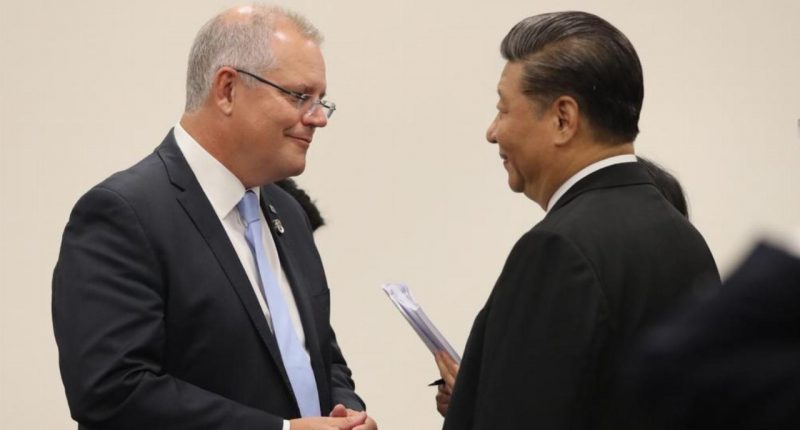
- Chinese investment in Australia fell to a six-year low of $1 billion in 2020, reflecting tensions between Canberra and Beijing
- The figure represents a 61 per cent drop compared to investments worth $2.6 billion in 2019
- The total number of investment projects came to just 20 last year — a stark contrast to a peak of 111 projects in 2016 worth $16.5 billion
- Of the $1 billion invested in 2020, 86 per cent came from Chinese companies already established within Australia
- In previous years, Chinese investments had penetrated almost every sector of Australia’s economy, but last year they dried up to cover just real estate, mining and manufacturing
Chinese investment in Australia fell to a six-year low of $1 billion in 2020, reflecting tensions between Canberra and Beijing as well as the impact of coronavirus.
According to the Australian National University’s (ANU) Chinese Investment in Australia database, this represents a 61 per cent drop compared to investments worth $2.6 billion in 2019.
The total number of investment projects came to just 20 last year — a stark contrast to a peak of 111 projects in 2016 worth $16.5 billion.
These projects have dried up to cover just three sectors: $461 million in real estate, $414 million in mining and $153 million in manufacturing. In 2018, investments in real estate alone were worth $1.1 billion.
“Without an active source of capital from China, we’re losing a big source of capital and it will devalue assets because we are losing a significant bidder,” said ANU’s East Asian Bureau of Economic Research director, Shiro Armstrong.
“$1 billion for Chinese investment in Australia is significantly low.”
Of last year’s investments, 86 per cent came from Chinese companies already established within Australia, meaning that purchases were made through Australian subsidiaries rather than by foreign firms directly.
It’s a trend that has continued from 2019, when 91 per cent of new Chinese investment was sourced from within Australia.
Armstrong noted that, based on data from the United Nations, foreign direct investment fell globally by 42 per cent.
“U.N. data is measured differently, but the fall in Chinese investment to Australia was much larger,” he continued.
“It reflects the effects of COVID but also more scrutiny of foreign investment by the Australian government, particularly that from China.”